After upgrading to ESXi version 5.5 and installing the current multipathing driver from EMC (PowerPath/VE 5.8/5.9) I encountered a problem with the local storage. EMC PowerPath claims the local storage and makes it inaccessible.
The ESXi Host is then unable to boot after trying claim the local devices.
It boots one last time after installing the driver but can’t access the local VMFS datastore. After a second reboot, an error message “No hypervisor found” is displayed in the VMware Hypervisor Recovery mode.
From now on, the ESXi Host does not boot and needs to be reinstalled.

The main cause for that issue can be found after the first (and last) reboot next to the PowerPath 5.8/5.9 installation in /var/log/vmkernel.log:
ALERT: PowerPath:Could not claim path vmhba1:C0:T0:L1. Status : Failure
WARNING: ScsiPath: 4693: Plugin ‘PowerPath’ had an error (Failure) while claiming path ‘vmhba1:C0:T0:L1′. Skipping the path.
ScsiClaimrule: 1362: Plugin PowerPath specified by claimrule 290 was not able to claim path vmhba1:C0:T0:L1. Busy
ScsiClaimrule: 1594: Error claiming path vmhba1:C0:T0:L1. Failure.
How resolve the situation?
DO NOT REBOOT the ESXi Host in that situation! Disable the claimrule for PowerPath, reclaim the local device, remove PowerPath, set the bootstate to 0 and reboot the ESXi Host:
- Identify the local Device with the vSphere Client. The local devices can be found in the Configuration Tab from the affected ESXi Host under Hardware -> Storage Adapters -> Paths
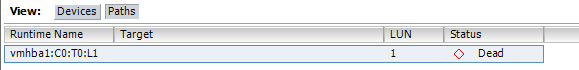
- Note the Adapter, Controller, Target and LUN ID (eg. vmhba1:C0:T0:L1)
- Open a SSH connection to the ESXi Host
- Disable all PowerPath ClaimrulesExample (‘esxcli storage core claimrule list’ output):
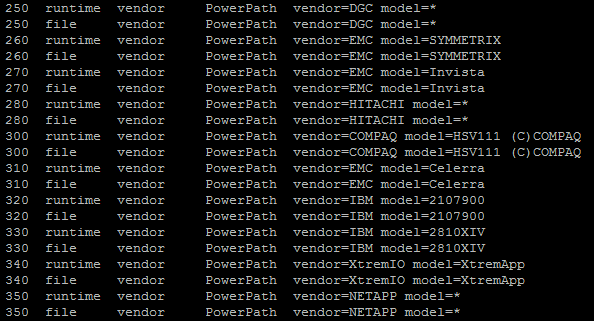
# List Claimrules (Verification step)
esxcli storage core claimrule list
# Remove the Rule
esxcli storage core claimrule remove --rule 250
esxcli storage core claimrule remove --rule 260
esxcli storage core claimrule remove --rule 270
[...]
# Reload the path claiming rules into the VMkernel:
esxcli storage core claimrule load
# Unclaim the affected device (eg. vmhba1:C0:T0:L1)
esxcli storage core claiming unclaim -t location -A vmhba1 -C 0 -T 0 -L 1
# Perform a rescan for the changes to take effect.
esxcli storage core claimrule run
- The local disk should now appear active:

- Remove PowerPath
esxcli software vib remove -n powerpath.cim.esx -n powerpath.lib.esx -n powerpath.plugin.esx
- Edit /bootbank/boot.cfg and set bootstate=0
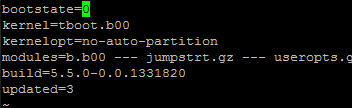
- Reboot the ESXi Host
The ESXi Host should now reboot and come up completely without PowerPath.
Fix / Workaround
To keep PowerPath away from the local storage you have to create a custom claimrule prior to install PowerPath 5.9.
1. Open a SSH connection to the ESXi Host
2. Create a Claimrule for the local devices to use the NMP multipathing driver. In that example, the rule is created for vmhba1:C0:T0:L1
esxcli storage core claimrule add --rule 110 -t location -A vmhba1 -C 0 -T 0 -L 1 -P NMP
3. Reclaim the affected device
esxcli storage core claiming unclaim -t location -A vmhba1 -C 0 -T 0 -L 1
esxcli storage core claimrule run
4. Install PowerPath/VE 5.8/5.9
esxcli software vib install -d /vmfs/volumes//EMCPower.VMWARE.5.9.b160.zip
5. Reboot the ESXi Host
6. Doublecheck the Claimrules. They have to look like this:
~ # esxcli storage core claimrule list
Rule Class Rule Class Type Plugin Matches
---------- ----- ------- --------- --------- ---------------------------------------
MP 0 runtime transport NMP transport=usb
MP 1 runtime transport NMP transport=sata
MP 2 runtime transport NMP transport=ide
MP 3 runtime transport NMP transport=block
MP 4 runtime transport NMP transport=unknown
MP 101 runtime vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
MP 101 file vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
MP 110 runtime location NMP adapter=vmhba1 channel=0 target=0 lun=1
MP 110 file location NMP adapter=vmhba1 channel=0 target=0 lun=1
MP 250 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=DGC model=*
MP 250 file vendor PowerPath vendor=DGC model=*
MP 260 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=EMC model=SYMMETRIX
MP 260 file vendor PowerPath vendor=EMC model=SYMMETRIX
MP 270 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=EMC model=Invista
MP 270 file vendor PowerPath vendor=EMC model=Invista
MP 280 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=HITACHI model=*
MP 280 file vendor PowerPath vendor=HITACHI model=*
MP 290 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=HP model=*
MP 290 file vendor PowerPath vendor=HP model=*
MP 300 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=COMPAQ model=HSV111 (C)COMPAQ
MP 300 file vendor PowerPath vendor=COMPAQ model=HSV111 (C)COMPAQ
MP 310 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=EMC model=Celerra
MP 310 file vendor PowerPath vendor=EMC model=Celerra
MP 320 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=IBM model=2107900
MP 320 file vendor PowerPath vendor=IBM model=2107900
MP 330 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=IBM model=2810XIV
MP 330 file vendor PowerPath vendor=IBM model=2810XIV
MP 340 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=XtremIO model=XtremApp
MP 340 file vendor PowerPath vendor=XtremIO model=XtremApp
MP 350 runtime vendor PowerPath vendor=NETAPP model=*
MP 350 file vendor PowerPath vendor=NETAPP model=*
MP 65535 runtime vendor NMP vendor=* model=*
~ #
Reboot the ESXi Host again to make sure it can boot. This workaround persists a reboot.


















